Princeton’s Scalable Recycling Solution to Reduce EV Battery Waste
Princeton NuEnergy (PNE) introduced a new method using low-temperature plasma-assisted separation (LPAS) to recycle EV batteries. This method employs plasma to remove impurities from battery components and recover anode and cathode materials for reuse in new batteries.
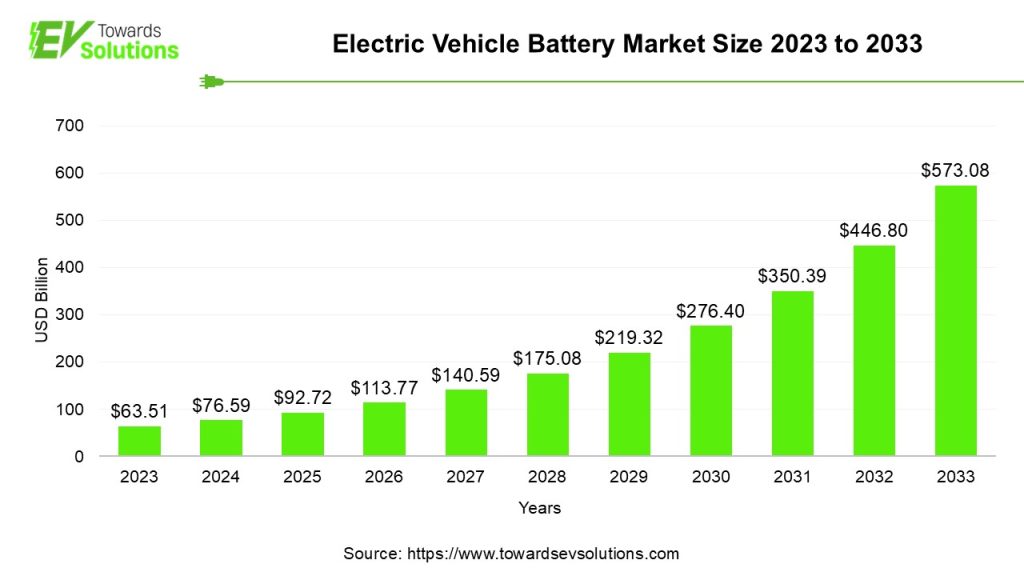
EV Battery Market
As per the Precedence Research’s detailed report on the global electric vehicle battery market size was valued at USD 63.51 billion in 2023 and is expected to hit around USD 573.08 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 25.1% over the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has led to increased concerns about battery waste. By reducing carbon emissions, EVs contribute to a sustainable future. As EV production accelerates, the need to dispose of or recycle lithium-ion batteries has become increasingly urgent.
Current recycling methods for EV batteries are limited in scope and effectiveness, underscoring the need to develop more robust and comprehensive recycling strategies. These strategies should focus on recovering valuable materials—such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel—and aim to minimize the ecological footprint associated with battery disposal. With projections indicating that as many as 150 million EV batteries may reach the end of their useful life by 2035, it is crucial to implement innovative solutions to handle this impending surge in battery waste. These solutions could involve advancements in recycling technology, enhanced battery design for easier disassembly and reuse, and improved regulatory frameworks to support sustainable practices. By prioritizing these innovations, we can significantly mitigate the environmental impacts associated with battery waste, ensuring a more sustainable future in the electric vehicle sector.
In 2020, around 550,000 electric vehicle (EV) batteries were disposed of, which has risen in subsequent years due to the increasing adoption of electric vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries, which power most electric vehicles, are classified as hazardous waste due to the potential environmental risks associated with their disposal. If these batteries are not disposed of correctly, they can release harmful chemicals into the environment, contaminating soil and groundwater. To mitigate the negative impacts of improper battery disposal, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established guidelines that advocate for the recycling and reusing of valuable metals in these batteries. Key materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel are critical components of lithium-ion batteries and can be extracted and repurposed. Recycling these metals may reduce the environmental hazards associated with battery waste and promote sustainability by conserving natural resources and minimizing the need for mining new materials. This approach can significantly contribute to a circular economy in the battery industry, ensuring that valuable resources are utilized efficiently and responsibly.
The initiative to recycle electric vehicle (EV) batteries marks a crucial advancement in sustainable practices, especially as the popularity of EVs continues to grow. However, it is important to note that most recycling facilities currently rely on processes such as shredding and high-temperature smelting. While effective at recovering valuable metals, these methods are highly energy-intensive and contribute to environmental pollution through the release of toxic emissions.
The two main methods employed in battery recycling are pyrometallurgy and hydrometallurgy. Pyrometallurgy utilizes elevated temperatures to melt down the battery materials and separate useful metals, a process that can create significant greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. In contrast, hydrometallurgy uses chemical leaching to extract metals at lower temperatures, which can be more environmentally friendly but still poses challenges with chemical waste management. Overall, while recycling EV batteries is a vital step toward reducing waste and promoting resource recovery, there is a pressing need to develop more efficient and environmentally sustainable recycling technologies.
We’ve prepared a service to support you. please feel free to contact us at sales@precedenceresearch.com | +1 804 441 9344
With a Master of Science in Statistics and over two years of expertise in the market research industry, Rushikesh brings a wealth of knowledge to the world of electric vehicle (EV) news. His passion for the automotive sector, combined with his statistical expertise, allows him to analyze trends, consumer behavior, and emerging technologies with precision. Rushikesh’s ability to dive deep into the numbers, yet communicate them in a reader-friendly manner, makes him a key voice in the fast-evolving EV industry.
Having spent his academic and professional career immersed in data-driven analysis, Rushikesh leverages his strong statistical foundation to offer insights that are both thorough and forward-thinking. His keen interest in the automotive industry, especially electric vehicles, positions him uniquely to understand not only the current landscape but also the trajectory of the sector as governments, manufacturers, and consumers increasingly lean towards sustainable transportation.



